幂等
编辑等 (UK: /ˌɪdɛmˈpoʊtəns/, US: /ˈaɪdəm-/) 是数学和计算机科学中某些运算的属性,它们可以多次应用,而不改变初始应用后的结果。 幂等性的概念出现在抽象代数(特别是投影仪和闭包运算符的理论)和函数式编程(其中它与引用透明性相关联)的许多地方。
该术语由美国数学家本杰明皮尔士于 1870 年在代数元素的上下文中引入,这些元素在提升到正整数幂时保持不变,字面意思是(具有的质量)相同的权力,来自 idem + potential(相同 + 权力 ).
定义
编辑集合 S {dISPlaystyle S} 的元素 x {diSPlaystyle x} 配备二元运算符 ⋅ {displaystyle cdot } 在 ⋅ {displaystyle cdot } 下被认为是幂等的如果
x ⋅ x = x {displaystyle xcdot x=x} 。
二元运算 ⋅ {displaystyle cdot } 被认为是幂等的,如果
x ⋅ x = x {displaystyle xcdot x=x} 对于所有 x ∈ S {displaystyle xin S} 。
例子
编辑- 在具有乘法的自然数的幺半群 ( N , × ) {displaystyle (mathbb {N} ,times )} 中,只有 0 和 1 是幂等的。 实际上,0 × 0 = 0 {displaystyle 0times 0=0} 和 1 × 1 = 1 {displaystyle 1times 1=1}。
- 在加法自然数的幺半群 ( N , {displaystyle (mathbb {N} ,} +) 中,只有 0 是幂等的。事实上,0 + 0 = 0。
- 在岩浆 ( M , ⋅ ) {displaystyle (M,cdot )} 中,单位元素 e {displaystyle e} 或吸收元素 a {displaystyle a} ,如果它存在, 是幂等的。 事实上,e ⋅ e = e {displaystyle ecdot e=e} 和 a ⋅ a = a {displaystyle acdot a=a}。
- 在群 ( G , ⋅ ) {displaystyle (G,cdot )} 中,恒等元素 e {displaystyle e} 是唯一的幂等元素。 事实上,如果 x {displaystyle x} 是 G {displaystyle G} 的一个元素使得 x ⋅ x = x {displaystyle xcdot x=x} ,那么 x ⋅ x = x ⋅ e { displaystyle xcdot x=xcdot e} 最后 x = e {displaystyle x=e} 通过在左边乘以 x {displaystyle x} 的逆元素。
- 在幺半群 ( P ( E ) , ∪ ) {displaystyle ({mathcal {P}}(E),cup )} 和 ( P ( E ) , ∩ ) {displaystyle ( {mathcal {P}}(E),cap )} 幂集 P ( E ) {displaystyle {mathcal {P}}(E)} 集合 E {displaystyle E } 与集合并集 ∪ {displaystyle cup } 和集合交集 ∩ {displaystyle cap } 分别,∪ {displaystyle cup } 和 ∩ {displaystyle cap } 是幂等的。 事实上,x ∪ x = x {displaystyle xcup x=x} 对于所有 x ∈ P ( E ) {displaystyle xin {mathcal {P}}(E)} 和 x ∩ x = x {displaystyle xcap x=x} 对于所有 x ∈ P ( E ) {displaystyle xin {mathcal {P}}(E)} 。
- 在幺半群 ( { 0 , 1 } , ∨ ) {displaystyle ({0,1},vee )} 和 ( { 0 , 1 } , ∧ ) {displaystyle ( 布尔域的 {0,1},wedge )} 分别具有逻辑析取 ∨ {displaystyle vee } 和逻辑合取 ∧ {displaystyle wedge }, ∨ {displaystyle vee } 和 ∧ {displaystyle wedge } 是幂等的。 实际上,x ∨ x = x {displaystyle xvee x=x} 对于所有 x ∈ { 0 , 1 } {displaystyle xin {0,1}} 和 x ∧ x = x {displaystyle xwedge x=x} 对于所有 x ∈ { 0 , 1 } {displaystyle xin {0,1}} 。
- 在布尔环中,乘法是幂等的。
- 在热带半环中,加法是幂等的。
- 在二次矩阵环中,幂等矩阵的行列式为 0 或 1。如果行列式为 1,则矩阵必然为单位矩阵。
幂等函数
编辑在幺半群 ( E E , ∘ ) {displaystyle (E{E},circ )} 中函数从集合 E {displaystyle E} 到自身(见集合取幂)与函数组合 ∘ { displaystyle circ } ,幂等元素是函数 f : E → E {displaystyle fcolon Eto E} 使得 f ∘ f = f {displaystyle fcirc f=f} , 即 f ( f ( x ) ) = f ( x ) {displaystyle f(f(x))=f(x)} 对于所有 x ∈ E {displaystyle xin E} 换句话说,每个元素 x ∈ E {displaystyle xin E} 的图像 f ( x ) {displaystyle f(x)} 是 f {displaystyle f} ) 的不动点。 例如:
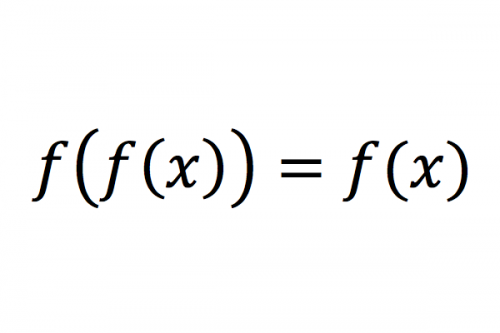
- 绝对值是幂等的。 实际上,abs ∘ abs = abs {displaystyle operatorname {abs} circ operatorname {abs} =operatorname {abs} } ,即 abs ( abs ( x ) ) = abs ( x ) {displaystyle operatorname {abs} (operatorname {abs} (x))=operatorname {abs} (x)} 对于所有 x {displaystyle x} ;
- 常量函数是幂等的;
- 身份函数是幂等的;
- 下限、上限和小数部分函数是幂等的;
- 群的幂集对自身的子群生成函数是幂等的;
内容由匿名用户提供,本内容不代表vibaike.com立场,内容投诉举报请联系vibaike.com客服。如若转载,请注明出处:https://vibaike.com/198206/
